
Secondary storage is preferred over primary storage due to the limited capacity and votality of primary storage.
SEQUENTIAL AND DIRECT ACCESS DEVICES:
SEQUENTIAL ACCESS STORAGE DEVICE:
A sequential access storage device is one in which arrival at a desired storage location is preceded by sequencing through other locations so that access time varies according to location.
Magnetic Tape is an example of sequential access storage device.
DIRECT ACCESS STORAGE DEVICE:
A direct access storage device is one in which we can reach and access any storage location at random, and approximately equal access time is required for accessing each location.
Magnetic disks,Optical disks and memory storage devices are examples of direct access storage device.
Magnetic media
Magnetic media stores data by assigning a magnetic charge to metal. This metal is then processed by a read head, which converts the charges into ones and zeros. Historically, magnetic media has been very popular for storing programs, data, and making backups. It looks set to continue in this role for some time. However, solid state technology is starting to be used more and more, storing programs and data on new devices such as mobile phones and cameras.
| Magnetic media | ||
|---|---|---|
| Device | Size | |
Hard Disk
| Up to 4 Terabytes | |
Magnetic Tape
| Up to 2 Terabytes | |
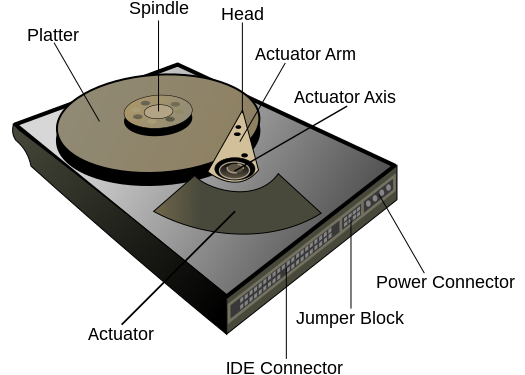
Hard disk
Hard disks are usually found inside computers to store programs and data. They are increasingly cheap and more and more companies are using them to back things up. Hard disks can vary in physical size with some disks getting as small as your thumb. The capacity of a commercial disk is currently up to about 4 terabytes allowing users to read and write to them.
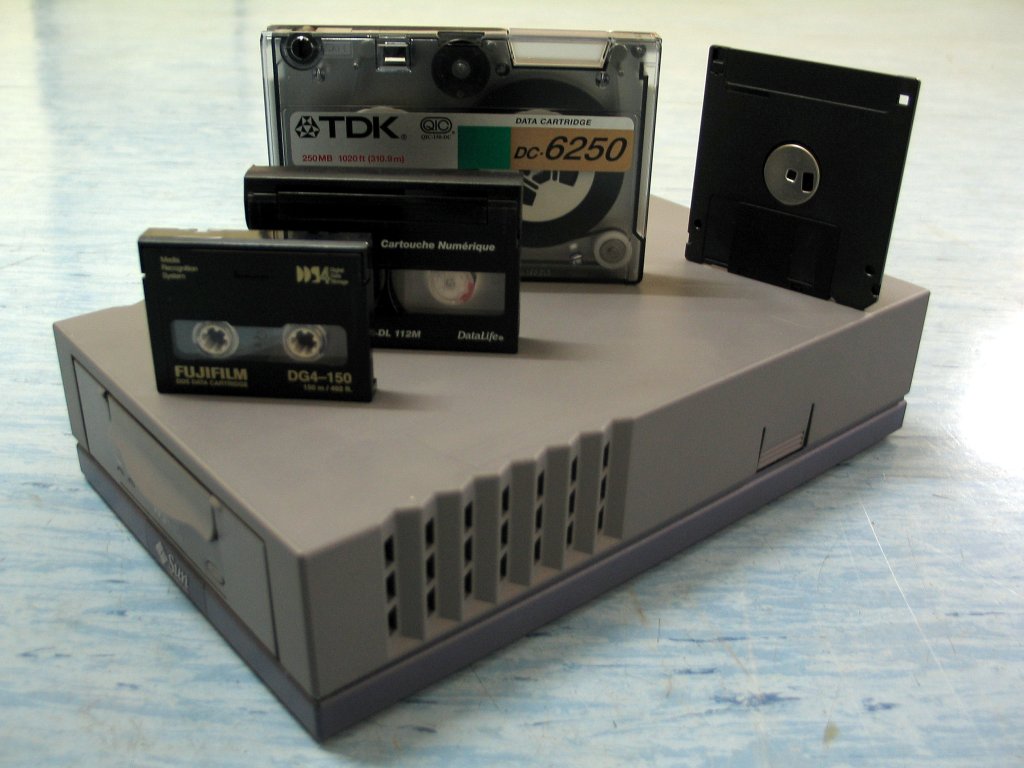
Magnetic Tape drive
Increasingly obsolete, the tape has been a medium to deliver software and back up data since the early days of computing. Nowadays they are used mostly for corporate backing up and archiving of data. Tapes are sequential data stores, meaning that if you had information stored at the end of the tape you would have to wind your way through the entirety of the tape before you could read it. There is no random access like with a hard disk! Tapes can be several terabytes in size and reading and writing can be very fast as long as you read or write continuous sections of the tape at once. It is

Optical media
Optical media works by creating a disc with a pitted metallic surface. There are several different types of disk out there ranging from 650 MB to 128 GB, with the pits and lands getting closer together for higher volume disks. The principle behind how each of them works is the same.
| Optical media | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Device | Type | Size | Image |
|
| 650 - 900 MB |  |
|
| 4.7 - 9.4 GB |  |
|
Re-Writable and Read Only versions available. Uses a blue laser, that is able to recognise smaller pits and lands, which allows for the pits and lands to be more closely packed, and so store more data
| 25 - 128 GB |  |
Solid-state memory
| Solid-state memory | ||
|---|---|---|
| Device | Description | |
USB flash drive
| Up to 256 GB | |
Memory card
| Up to 256 GB | |
USB (memory stick) Flash Drive
 Internals of a typical USB flash drive | |
| 1 | USB Standard-A plug |
|---|---|
| 2 | USB mass storage controller device |
| 3 | Test points |
| 4 | Flash memory chip |
| 5 | Crystal oscillator |
| 6 | LED |
| 7 | Write-protect switch (Optional) |
| 8 | Space for second flash memory chip |
USB Flash drives are solid state, that means that there are no moving parts. This is very useful for seek times as we don't have to wait for mechanical movement, meaning seek time is very low and it allows for fast Random Access Memory. Flash drives can be set to read only mode, but they will always allow for reading and writing. The size of flash drives is not as great as a Hard Disk and they are generally much more expensive per megabyte
- put drive into USB socket
- USB driver loads, providing the computer with code on how to read and write from the USB
- The USB is read, giving information on the file and folder structure (File Allocation Table) to the Computer
- [Reading] The user chooses to open a file, the Computer sends the address wanted to the USB port
- [Reading] The USB returns the data at the location requested
- [Writing] The computer sends data to the USB port where it is place into empty space on the drive
- [Writing] The computer then requests a new version of the file and folder structure
Advantages:
Limitations:
Memory cards
Work in much the same way as a Flash drive and can often be converted into Flash Drives. They have different connectors and are generally smaller than USB Flash drives allowing for them to be used in cameras, mobile phones and game consoles.

.

No comments:
Post a Comment